Route 53
What is DNS?
Domain Name Servers (DNS) are a way to resolve website URLs to IP addresses.
For example translating www.google.com to it’s IP address of 172.217.18.36.
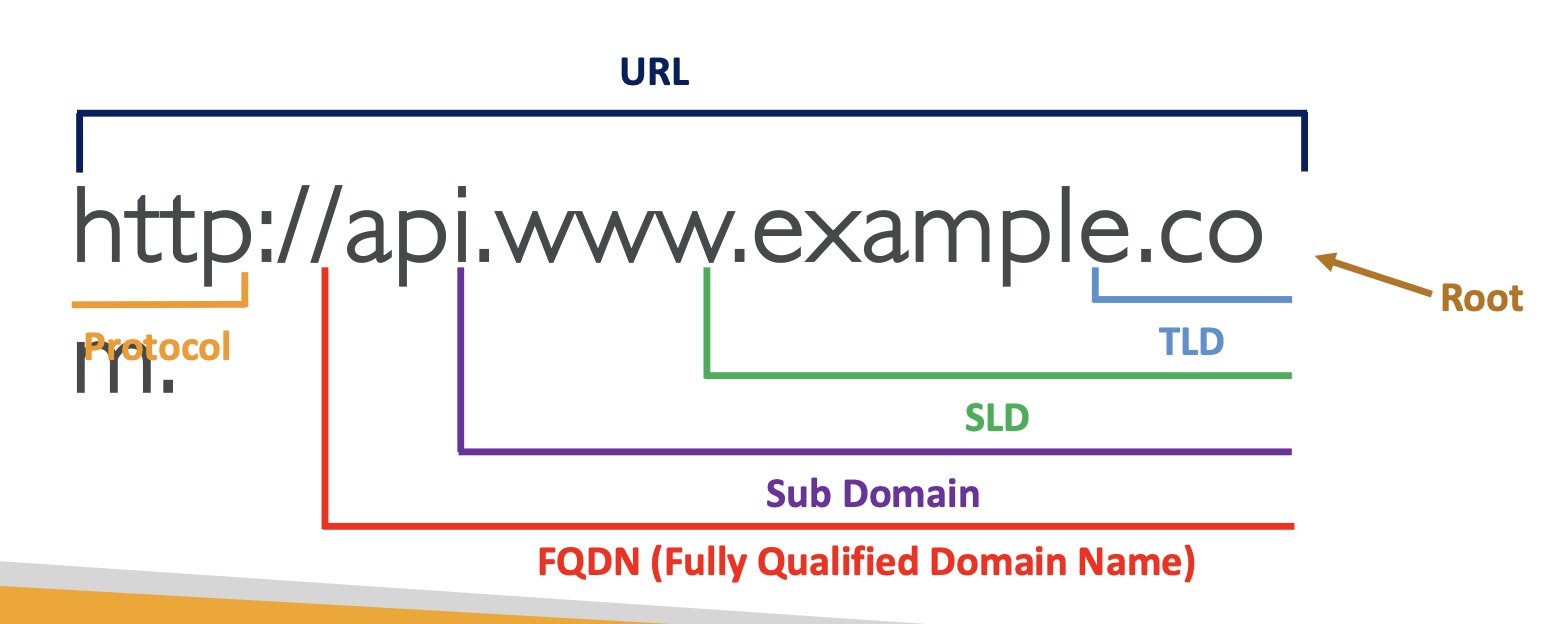
URL breakdown
This is the breakdown of a URL:
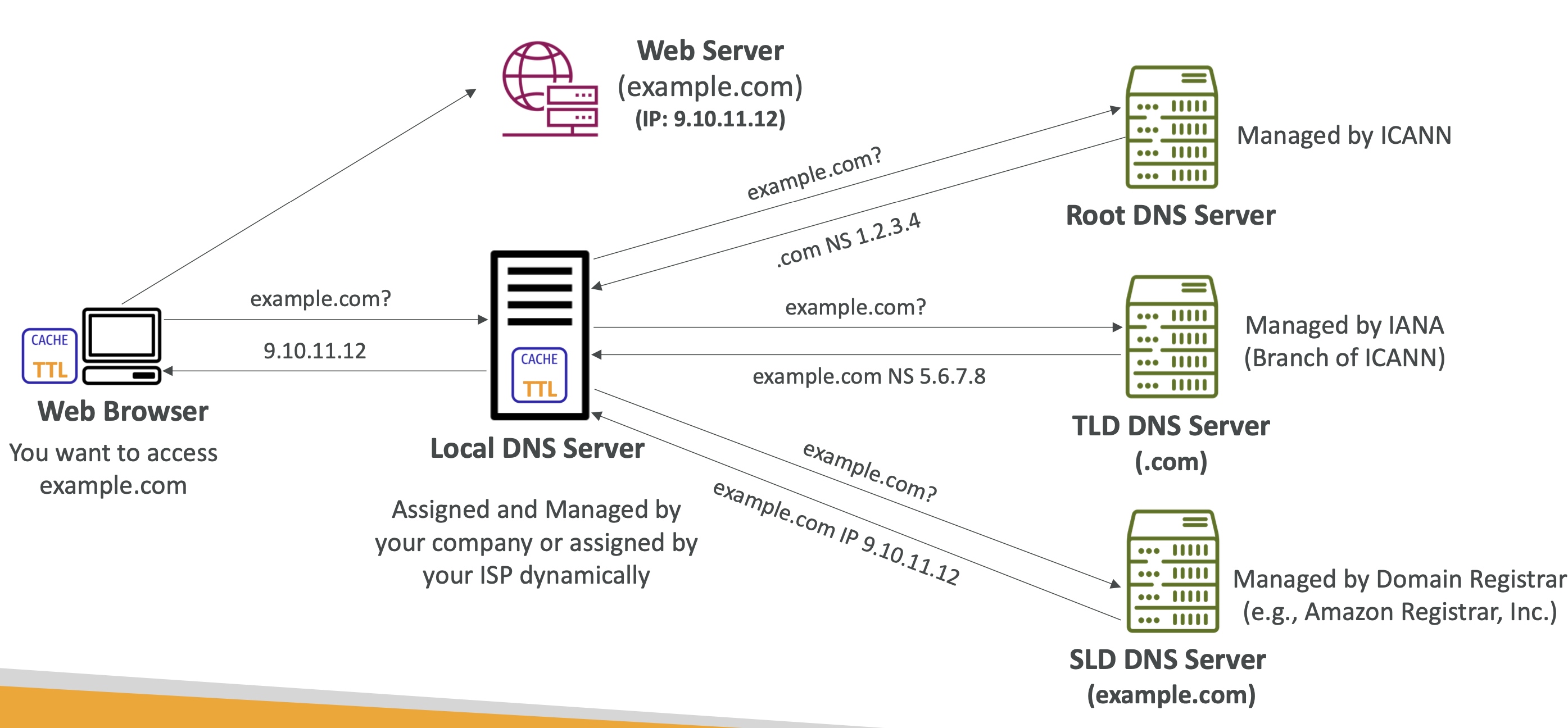
How DNS works
The process of resolving an IP address takes many steps, including reaching out to many servers:
Amazon Route 53
This is Amazon’s DNS service and domain registrar.
Requests to websites registered with Route 53 will go to Amazon’s Route 53 DNS.
Route 53 DNS records
DNS records are instructions stored on DNS records that allow us to connect domain names to IP addresses. Route 53 is authoritative, meaning you have control over your DNS records.
Route 53 supports the following records:
- Must know: A / AAAA / CNAME / NS
- Advanced: CAA / DS / MX / NAPTR / PTR / SOA / TXT / SPF / SRV
Record types
- A: maps a domain name to an IPv4 address
- AAAA: maps a domain name to an IPv6 address
- CNAME: maps a hostname to another hostname. C stands for “canonical” and CNAMEs allow you to create aliases for your domain names. For example, you could point example.domain.com to domain.com to resolve the IP address, instead of to the IP address itself. The IP resolution will happen at domain.com
- NS: Name Servers for the hosted zone. This controls how traffic is routed for the domain.
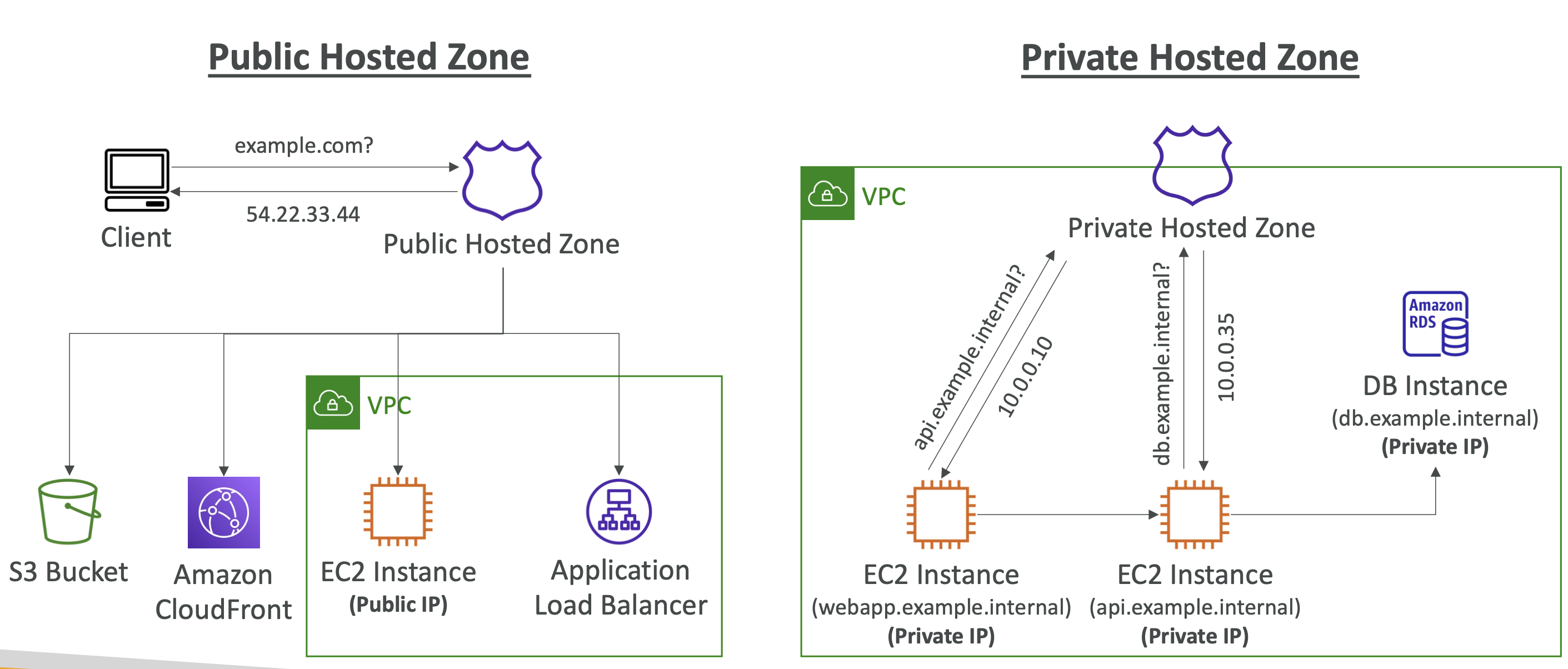
Route 53 - Hosted Zones
Hosted Zones are containers that define how to route traffic to a domain and subdomains. For example you can have:
- Public Hosted Zones: records that define how to route public domain names
- Private Hosted Zones: records that define how to route private domain names